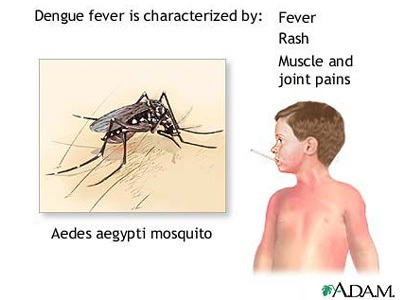
Dengue fever are dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF) are acute febrile diseases that are prevalent in the urban areas of developed tropical countries. Dengue is similar to malaria except that malaria is mostly contained in more rural areas. It is caused by a Flavivirus transmitted to humans by female Aedes aegypti mosquitoes that feed during the day.
Origins of Dengue
Dengue fever first occurred as a simultaneous epidemic in Africa, Asia, and North America in the late 1700s and was identified and named in 1779. It was in the 1950s and 1970s when another global onslaught happened. It began in Southeast Asia but spread widely soon after. Dengue fever became more common with sporadic outbreaks happening through the years.
Scientists and pharmaceutical companies have been steadily developing a cure for the actual virus itself but as of present, there are still no substantial results. Most medicine and treatments are focused more on decreasing the discomfort of patience brought by the fever.
How is dengue fever contracted?
The virus is contracted from the bite of a striped Aedes aegypti mosquito that has previously bitten an infected person. The mosquito flourishes during rainy seasons but can breed in water-filled flower pots, plastic bags, and cans year-round. One mosquito bite can cause the disease.
The virus is not contagious and cannot be spread directly from person to person. There must be a person-to-mosquito-to-another-person pathway.
How is dengue fever diagnosed?
The diagnosis of dengue fever is usually made when a patient exhibits the typical clinical symptoms of headache, fever, eye pain, severe muscle aches and petechial rash and has a history of being in an area where dengue fever is endemic. Dengue fever can be difficult to diagnose because its symptoms overlap with those of many other viral illnesses, such as West Nile virus and chikungunya fever.
In 2011, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a blood test to diagnose people with dengue fever, called the DENV Detect IgM Capture ELISA. The FDA notes that the new test may also give a positive result when a person has a closely related virus, such West Nile disease.
What is the treatment for dengue fever?
Because dengue fever is caused by a virus, there is no specific medicine or antibiotic to treat it. For typical dengue, the treatment is purely concerned with relief of the symptoms. Rest and fluid intake for adequate hydration is important. Aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should only be taken under a doctor’s supervision because of the possibility of worsening bleeding complications. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) and codeine may be given for severe headache and for joint and muscle pain (myalgia).
How can dengue fever be prevented?
The transmission of the virus to mosquitoes must be interrupted to prevent the illness. To this end, patients are kept under mosquito netting until the second bout of fever is over and they are no longer contagious.
The prevention of dengue requires control or eradication of the mosquitoes carrying the virus that causes dengue. In nations plagued by dengue fever, people are urged to empty stagnant water from old tires, trash cans, and flower pots. Governmental initiatives to decrease mosquitoes also help to keep the disease in check but have been poorly effective.
To prevent mosquito bites, wear long pants and long sleeves. For personal protection, use mosquito repellant sprays that contain DEET when visiting places where dengue is endemic. There are no specific risk factors for contracting dengue fever, except living in or traveling to an area where the mosquitoes and virus are endemic. Limiting exposure to mosquitoes by avoiding standing water and staying indoors two hours after sunrise and before sunset will help. The Aedes aegypti mosquito is a daytime biter with peak periods of biting around sunrise and sunset. It may bite at any time of the day and is often hidden inside homes or other dwellings, especially in urban areas.
There is currently no vaccination available for dengue fever. There is a vaccine undergoing clinical trials, but it is too early to tell if it will be safe or effective. Early results of clinical trials show that a vaccine may be available by 2015.


I Really Like your This Post Best Of luck.. 🙂
Croteles is best Homoeopathic Medicne for dengue fever