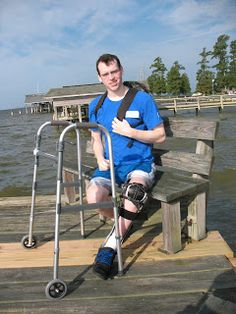
In a pilot study of postpolio syndrome patients, a multidisciplinary rehabilitation approach involving tailored physiotherapy exercises has shown to have significant benefit on muscle endurance, exertion, and depression levels for up to 6 months.The program begins by determining the polio survivor’s maximum exercise capability with the help of the clinic physical therapist. The type of exercise can be in a pool or on dry land, using an arm erqometer or an exercise bicycle, depending on the individual’s abilities and preferences. If one prefers swimming, the maximum number of laps that the patient can swim is used as the maximum exercise capability. If the survivor has considerable residual weakness and is only able to swim one lap in half an hour, then the amount of time actively swimming can be used as the maximum exercise capability rather than the number of laps.Physiotherapy is a cornerstone of management of polio and post polio syndrome.
Types of polio
Spinal Paralytic poliomyelitis: In this the motor neurons in the anterior horns of spinal cord are affected. Paralysis is usually asymmetrical, predominantly involves proximal muscle with pain and tenderness. Most commonly it affects the leg. Extent of weakness can vary from a single muscle group to complete tetraparesis.
Bulbar Paralytic poliomyelitis: It occurs due to damage to the medulla, pons and midbrain with dysfunction of the cranial nerve nuclei and respiratory and vasomotor regulating centres in the medulla. It can lead to respiratory muscle failure, distress of respiratory control, dysphagia, dysphonia and dysarthria. Cardiovascular, sweating and gut mobility disturbances may occur.
Bulbospinal paralytic poliomyelitis: It is also known as respiratory poliomyelitis. It has symptoms both of spinal cord and bulbar poliomyelitis. It affects the part of spinal cord C3 to C5 segments and causes paralysis of the diaphragm. Dysphagia and respiratory failure follow.
Polio encephalitis: There is inflammation of motor neurons within the brain stem, motor cortex and the spinal cord. It leads to the stiffness of back and neck, muscle cramps, headaches and paraesthesias. Paralysis occurs within 10 days after symptoms develop progress in 2 to 3 days and complete by the time fever subsides.
The treatment involves 3 steps:
Cardio Exercise : According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, cardio training is typically more often recommended to post-polio patients over resistance training exercises. Heavy lifting is not advised since over training may further weaken the muscles rather than strengthen them. The ideal cardio exercise for post-polio patients is swimming since you are not putting any stress on the muscles and joints.
Yoga : Yoga is a recommended form of exercise by the Post-Polio Health International organization. Benefits of yoga include better balance, improved flexibility and a reduction in pain symptoms. If you are taking a class, take a gentle or beginner’s class that has you do a mix of stretching, deep breathing and meditation exercises. In the class, you should have access to a chair or wall for support during the moves if you need it.

5